The beginning of a new era has already begun worldwide, known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution. It is about changing the basic way of life of the human race. We do not yet know how this will unfold, but one thing is clear: the response must be unified from all sectors of life.
We may have heard about this new word through different media, but how much do we understand its implications and future? I am writing this article to discuss what will happen in this new age, what we will get out of it, and how to adapt to this new ecosystem.
Origins of the Term Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Founding Father of The World Economic Forum (WEF), Professor Klaus Schwab, first coined the term ‘Industry 4.0’ in 2016. As Professor Klaus says, 4IR combines physical, digital, and biological fields with emerging technologies. The emerging technologies he mentioned are Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), 3D Printing, Genetic Engineering, Quantum Computing, and others.
In the 4IR era, engineers can combine these technologies to improve communication and Automation to achieve better results. I will discuss these emerging technologies to see how they can be connected and how they will change the world.
Soon, the 4th Industrial Revolution will change the nature of the whole working system that we know of. It will also affect people’s lives from scratch. So, the world must be prepared to adopt these technologies for long-term success.
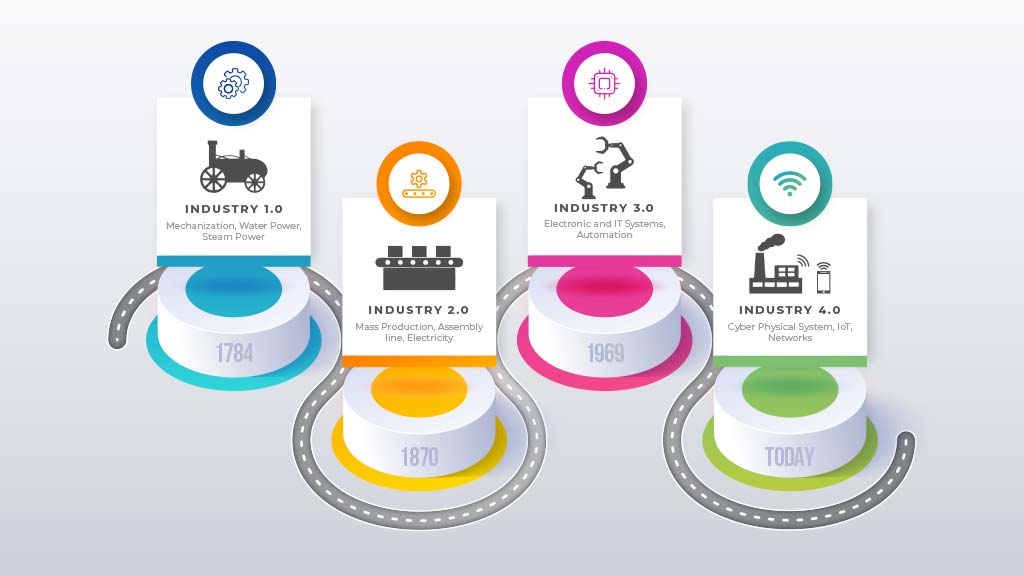
After three big revolutions, now the Fourth Industrial Revolution is happening. Usually, Industrial Revolutions change the way industries operate with the existing technologies. But, before we go into depth to discuss this revolution, we should understand those three big revolutions.
So, let’s understand how the previous revolutions happened and brought the world to this stage.
First Industrial Revolution
Early humans relied on human and animal labor to do tasks. For example, they used to make their clothes by spinning yarn and weaving cloth.
The First Industrial Revolution changed a lot of this. It started in 1760 in England, increasing the living standards.
The First Industrial Revolution led to the increased use of machinery in place of manual labor. The steam engine was the most famous invention at that time. James Watt. invented this engine that changed everything. After that invention, people could run machinery such as vehicles, factories, etc., through Steam Engine.
Soon, the steam engine found use in rail locomotives and steamboats for travel. Machine tools using steam engines also increased the production of goods.
Let’s explore the notable inventions during the First Industrial Revolution.
Notable Inventions of the First Industrial Revolution
The First Industrial Revolution had improvements in chemical manufacturing. New chemicals introduced included Sodium Carbonate. This chemical has found use in the glass, textile, soap, and paper industries.
Then, the textile industry got a boost from steam engines. Power looms worked faster than humans to produce more cloth. New chemicals also helped in bleaching the clothes.
However, Iron got more important in this period. At that time, Iron was the stronger metal, and it found use in many industries.
The First Industrial Revolution occurred till about 1840. After this period, there was a slowdown in scientific inventions. But, in the next 30 years, many new things happened. Then, in about 1870, people invented more revolutionized tools that led to the Second Industrial Revolution.
Second Industrial Revolution
After the Second Industrial Revolution, it took industry further with many important inventions. At that time, the communication system was very widespread. Other facts made people more modern.
Invention of Electricity
The invention of electricity or Electrification started in the 1880s. The first electric lights helped light factories, replacing hazardous gaslighting. Besides, the induction motor-powered machines became more efficient than the steam power.
Invention of Steel
The Bessemer process was the first economical process to mass-produce steel. Steel was stronger than Iron and cheaper to produce. As a result, the US rail network utilized steel. Thus, large skyscrapers, bridges, and ships were built using steel.
Communication System
The telegraph network improved communications. Britain, USA, and France were the leaders in this technology. Then telephones took control over telegraphs. Thus, real-time communication became common and more hassle-free.
Assembly Line
Assembly lines started with the Electrification of factories using machine tools. As a result, common goods became common and cheaper. The most famous example is the Ford Model T. Besides, automatic production of goods has been easier and faster than ever before.
The Second Industrial Revolution took civilization to greater advancement. It took less time than the first revolution to reach the third industrial revolution. However, all the unique inventions at the end of the Second Industrial Revolution started the Digital Revolution in the mid-20th century.
The Third and Digital Revolution
The Third Industrial Revolution is also called the Digital Revolution. A major reason is that digitization took over mechanical and analog technologies. Therefore, the two important pillars of the third industrial revolution are microelectronics and the Internet.
Microelectronics
The invention of the transistor in early 1947 led to digital computers. Computers can solve complex calculations faster than humans. After the invention of ICs and Microchips, Computers became more powerful. Thus, Computing became more involved in Industries and daily lives.
The Internet
The most amazing discovery in the world so far is the Internet. Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee, also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist known as the World Wide Web or the Internet inventor.
After more development of the WWW, computers can now communicate over long distances. The WWW made sharing of information and other data easier than ever.
The usage of electronic devices became more common during the Third Industrial Revolution. The start of the 21st century is the era of smart devices such as smartphones, smart computers, smart laptops and more. Combining smart devices and other network technologies takes us to an advanced era: the Fourth (4th) Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0.
Fourth Industrial Revolution / 4IR / Industry 4.0
The Fourth Industrial Revolution combines different technologies. Thus, the physical, digital, and biological domains have all merged.

Cyber-Physical Systems, the Internet of Things, and Cognitive Computing are the three main pillars of 4IR or Industry 4.0.
Microelectronics was the greatest invention in the Digital Revolution. Now they are getting even smaller. According to American engineer Gordon Moore’s Law, the number of transistors placed on ICs doubles every two years.
Let’s explore Some of the technologies that will reign in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Robotics and Automation
- Autonomous Vehicles
- 3-D Printing
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Quantum Computing
- Materials Science
Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution
The technologies driving Industry 4.0 are grouped into three categories. They are Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Cognitive Computing. In addition, these technologies have many sub-technologies under them. Thus, we can call this era a technological revolution.

Cyber-Physical Systems in The Fourth Industrial Revolution
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) combine many physical systems. A computer controls this group of devices.
Combining devices allows them to work together to do various tasks. The coordination and efficiency of these devices are improving. As a result, the Fourth Industrial Revolution can use combined systems.
Examples of Cyber-physical Systems (CPS) are:
Robotics and Automation
Automation in factories is becoming more common due to improvements in robotics technology. Using robots to perform specific tasks helps accuracy and reduces the required time.
Robots now do repetitive tasks such as the assembly of cars. In addition, robotics can assist in surgery, reducing human error. As a result, millions of lives will be saved in the future.
Robotics is an important aspect of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Using it frees up valuable resources for other tasks too.
Autonomous Vehicles or Smart Cars
A self-driving automobile, also known as an Autonomous Vehicle (AV), driverless car, or robotic car (Robo-car), is a ground vehicle that can sense its surroundings and move safely with little or no human intervention. The future of this technology might have ramifications in various sectors and situations.
The computers in the vehicle can use the data from the sensors to react as needed.
Similar technology is also used in autonomous drones. For example, a drone can deliver life-saving medication without delays due to traffic. As Artificial Intelligence improves, autonomous vehicles will also become more reliable and efficient.
Smart Grids
A smart grid is an electrical system with many operational and energy-saving features, such as:
- Infrastructure for advanced metering
- Home control and demand response
- Smart appliances and load control switches
- Renewable energy resources
- Resources that are low on energy
Smart Grids have sensors and an Internet connection to them. Machine Learning (ML) makes decisions on how the Grid operates. As a result, energy requirements, maintenance, and grid optimization occur.
Wastes are also reduced by producing the correct energy through smart grids.
Internet of Things (IoT) in the Fourth Industrial Revolution
IoT includes a network of objects embedded with electronics and network connectivity. As a result, this enables the “object” to collect and exchange data.
In addition, IoT provides many opportunities in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Besides, IoT has many real-life applications already, such as the emergence of smart homes.
For example, smart homeowners can control their IoT devices remotely.
The IoT (Internet of Things) Life Cycle involves the following:
- Collect: The sensors and electronics in the object always collect real-time data.
- Communicate: The object relays information to the network via the cloud.
- Analyze: The data analysis reveals useful information that the software can use.
- Act: The IoT system takes action based on the collected data and information.
IoT (Internet of Things) Implementation includes the following:
Smart Homes
When connected, home gadgets are an essential component of the Internet of Things era. Now, lighting, temperature, entertainment systems, and appliances can be monitored and controlled by a home automation system.
It is a central hub that connects smart home devices so that users can access the devices through their smartphones.
A smart home network includes lighting, air conditioning, and smart kitchen appliances. Furthermore, CCTV cameras and motion sensors will enhance security. Finally, improvements in AI can improve these smart homes even better.
However, the only limitation of the possibilities in the Fourth Industrial Revolution is imagination.
IoT Implementation in Healthcare
The Internet of Things (IoT) has helped remote monitoring of patients possible. So, personalized care exists, and there is no need to visit distant hospitals.
To include smartwatches have blood pressure monitors and heart rate monitors embedded. As a result, the user can track their vitals without visiting a doctor.
Monitoring the patients remotely also helps the patient and the doctor.
The hospitals can maintain an inventory monitoring system on their servers. These will happen in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and many have already implemented these technologies.
IoT Implementation in Agriculture
IoT has enabled farmers to track their crops better. So, farmers can provide the same care as the crops need. Besides, connecting a farm to the Internet can also reduce manual maintenance.
Analysis of the data gathered on crops and animals can provide new solutions. Thus, using AI(Artificial Intelligence) will help find efficient ways to operate the farm in the Agricultural sector.
As a result, food security will improve in the Fourth Industrial Revolution by implementing IoT in the Agricultural sector.
Cognitive Computing
Cognitive Computing is where computerized models can replicate the human thought process in complicated settings. The solutions may be ambiguous and unclear, but it is a very effective technology in this era.
Watson, IBM’s cognitive computer system, is intimately connected with the term. Expert systems, Neural Networks, Robots, and Virtual Reality are all used in Cognitive Computing, and many of the same enabling technologies are used to power cognitive applications.
Cognitive Computing combines hardware and software to work like a human brain. The main branch of cognitive Computing is Artificial Intelligence. Under it falls:
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Natural Language Processing
- Computer Vision
- Speech Recognition
These technologies have been used in the Retail, Power, Healthcare, and Education sector.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
AI is sometimes called the Fourth Industrial Revolution since it plays a huge role. The AI aims to simulate human thinking and behavior and apply them to machines. As a result, computers can solve complex problems that humans take years to solve.
Current applications are basic, such as Chatbots. Customer support and smart assistants like Amazon’s Alexa use AI (Artificial Intelligence).
In the 4IR era, research on AI can discover many powerful applications. These can range from discovering new medicines and vaccines to solving Global crises like pandemics.
How does Machine Learning work?
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset technology of AI. ML systems gather data and then “learn” how it works. Thus, the computer can make predictions and decisions based on historical data. ML is currently used by tech giants Google, Amazon, Facebook, etc.
A great example of ML is facial recognition programs. Millions of human faces are input into the ML system so that the ML program can analyze and learn from the data.
Like AI, Machine Learning has tremendous potential in the 4IR era. ML can analyze data to find patterns, solving many problems. For example, a person’s chromosome and DNA makeup can be analyzed using ML.
What is Computer Vision?
Computer Vision is another field of Artificial Intelligence. The computer trains to get information from digital images taken from cameras. It is a method to allow the computer to “see” and then interpret that data.
Computer vision is almost the same as machine learning. One application of computer vision is the real-time translation of data.
Google Lens is an example of that. In Lens, the user can point their camera at a text in one language. Then the computer vision system can instantly translate it to their desired language.
The Lens can also identify objects such as plants and animals, the current consumer usage of computer vision.
Further research will improve this technology manifold. For example, self-driving cars will become more reliable in this new era.
Other technologies that will be Popular in the Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Fourth Industrial Revolution introduced many new technologies. I have already discussed the major ones above. Let’s learn about other technologies that will gain huge popularity in the 4th Industrial Revolution.
3-D Printing Technology in the 4IR Era
3-D Printing is a concept that can revolutionize the manufacturing industry. In this concept, computer-Aided Design (CAD) software can create models and automate the entire process of “making” the product.
3-D Printing uses a method of manufacturing called Additive Manufacturing. The product is created layer by layer, which reduces waste.
In addition, traditional manufacturing uses many specialized tools and fixtures. And they will stay in the museum forever in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
3-D Printing also enables a method called “rapid prototyping.” It is where Prototypes are quickly manufactured using 3-D Printing so that many iterations are done quickly.
Nanotechnology in the 4th Industrial Revolution
Nanotechnology is using matter on an atomic level to produce new materials. The potential uses of nanotechnology are vast, from nanomedicine to nanoelectronics and nanomaterials. Let’s learn more about Nanotechnologies.
Nanomedicine
Brain treatment found uses for nanoparticles. So, Nanomedicine is some very small particles that can deliver drugs to areas not usually accessible. For example, some solutes cannot pass through parts of the brain, but nanoparticles can.
Nanomaterials
Advances in nanotechnology have added new properties to the material. For example, construction materials like cement and steel are stronger and more durable.
These improvements can make structures even more resilient to natural disasters like earthquakes.
Nanoelectronics
Electronics are getting ever smaller thanks to nanotechnology. As a result, electronics are now placed in ever-smaller devices. An example of this would be solar panels. Having small sheets of PV cells allows for more efficient energy generation.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology makes modifications to living organisms. Changing them makes them better suited to a specific purpose.
And Microorganisms help in the manufacturing of organic products such as milk and cheese. In agriculture, there are Genetically Modified (GM) crops too. These crops have more nutrients and have higher harvest yields.
Besides, Genetic engineering can eliminate many diseases which have a genetic component. For example, the Human Genome Project in the ’90s sequenced human DNA. So, now scientists can analyze specific genomes to find the cause of diseases.
How Much of 4IR Has the World Adopted so Far?
Technologies involved in the Fourth Industrial Revolution have existed for many years now. Yet, the world has been slow at adopting these technologies. What are the obstacles?
There are some, especially in third-world countries. But many developed countries have already adopted Industry 4.0 in several areas.
4IR in Industrial Sector
Industry 4.0 is an alternate name for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Physical and manual skills have been less in demand in developed countries for 15 to 20 years.
A report published by McKinsey and Company shows that the demand for physical and manual skills will decline by 11% in the US from 2016 to 2030. Reference: Automation and the future of the workforce
Robotics is being used in many industries too. For example, in Healthcare, the da Vinci Surgical System helps a lot in surgery.
A surgeon controls the robot for complex and precise surgeries. In addition, the robot has found use in cardiac valve repair too.
Developed countries are also using Autonomous Robots in manufacturing. For example, robots help in repetitive tasks such as car painting, welding, assembly line work, and more in the automotive industry.
4IR in the Tech Industry
Tech giants like Google, Amazon, Facebook, and Alibaba are implementing new technologies in their industry. For example, for e-commerce, Amazon and Alibaba use AI to predict what their customers can buy.
4IR in Home Automation
IoT has helped spread home automation. Currently, various devices in the home are using IoT-powered devices. For example, thermostats, lights, garage doors, security systems, and more can be controlled using smartphones.
This industry is still in its infancy. Advancements in AI will enable these systems to become even smarter.
Despite varying uses of technology, most of the world is yet to take the full opportunity. So far, most wealthy countries such as the EU Nations, China, the US, and Singapore have adopted the 4IR/Industry 4.0.
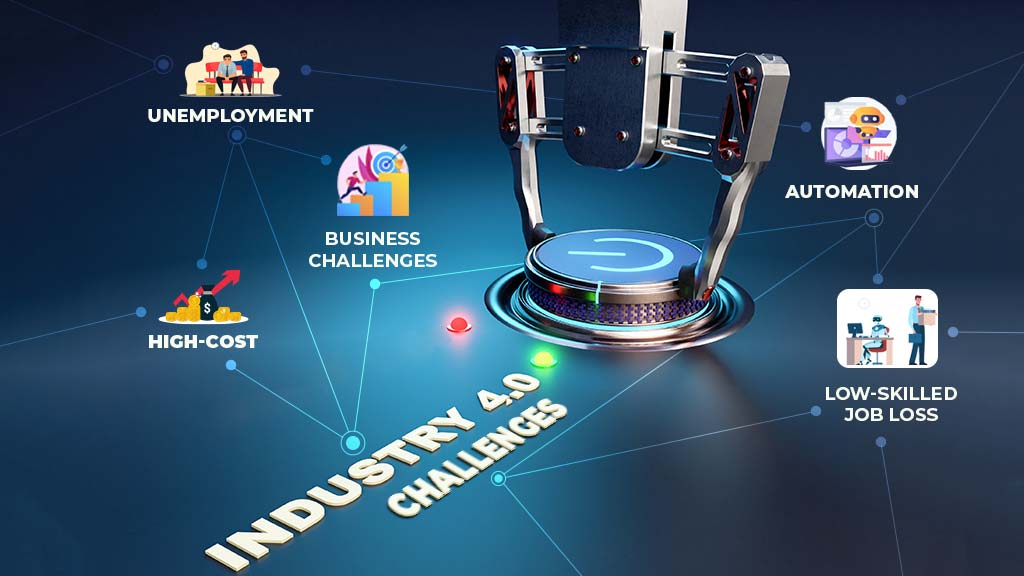
Challenges in Implementing the Fourth Industrial Revolution
The current trend is to embrace the changes of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Yet, this isn’t without major hurdles. So, likewise, hurdles need to be overcome for a sustainable implementation of 4IR.
The challenges we will face in adopting Fourth Industrial Revolution are economic, social, political, and organizational challenges.
Economic Challenges of the 4th Industrial Revolution
The cost of implementing the new technologies involved is high. Therefore, economic hurdles need to be overcome to implement 4IR globally.
High-Cost
Introducing new technologies takes much investment from the concerned parties. For example, in Artificial Intelligence, researchers use thousands of terabytes of data. This data is then stored in large data centers, such as those owned and operated by Google and Amazon.
Data centers contain expensive hardware equipment such as servers and computers. They also use large amounts of electricity. For AI to become common, countries worldwide need to invest in infrastructure.
Hence, a big barrier to implementing new technologies is the high cost.
Unemployment
Another challenge is that governments may be reluctant to invest lots of money. An example is countries with a large population working in manual labor.
On the other hand, manual labor includes farming and factory workers. So, these countries will be hesitant to invest in 4IR due to fear of rising unemployment.
Business Challenges
Businesses need to change their business models in the new era. Yet, this is difficult as the benefits aren’t always clear. Without forward-thinking leaders, it will be difficult for businesses to adopt 4IR.
These economic challenges need consideration for the Fourth Industrial Revolution to progress.
Social Challenges of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Social challenges include challenges to people and society in general. There are many factors of 4IR that will highly impact our social life.
Homes
New technologies such as IoT will make the world more connected. However, having homes connected to the Internet comes with challenges.
These threats include hackers and thieves accessing personal data. As the 4IR progresses, people may distrust these technologies more. Reasons for this involve widespread surveillance, including facial recognition and more. Police forces use facial recognition to track the population.
Low-skilled Job Loss
Increased Automation will become more common as the Fourth Industrial Revolution progresses. As a result, people from low-skilled backgrounds are at risk of being vulnerable to job losses.
Therefore, governments need to find a suitable solution for the ultimate job losses. Otherwise, crime, protests, and homelessness may increase among blue-collar workers.
Political Challenges of the 4th Industrial Revolution
From the perspective of governments, embracing major changes doesn’t happen overnight.
Most governments don’t have the political infrastructure to make the required changes. Some examples include the lack of regulations, standards, and certifications.
Regulations are how a country controls the way its nation operates. Therefore, governments need to introduce regulations and standards for implementing 4IR. Currently, only the big nations such as those in the EU, the US, and a few others are doing so.
Besides, introducing regulations and standards will tackle other problems. These problems include data security and legal issues, which are integral in this new revolution.
Digital Data plays a crucial role in benefiting or harming people. So, preventing misuse of the data needs to be at the forefront of the agenda for the leaders.
Organizational Challenges of the 4th Industrial Revolution
A major part of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is the introduction of Automation. These will reduce the human element to lots of jobs and everyday activities.
For example, going to a restaurant will mean ordering food from a robot waiter. The waiter will relay the order to a robot cook, resulting in the food served by the robot waiter. As a result, humans will become ever reliant on machines, computers, and the Internet.
Automation simplifies the process but raises a major organizational challenge. Those responsible need to ensure the automated system’s reliability, security, and stability.
Failing this will result in a complete breakdown of many of the basic aspects of societies. These include important activities such as banking, travel, and healthcare services.
A lack of skilled workers is another challenge for organizations. Training a large number of people is an expensive and time-intensive process. Thus, workers’ abilities will set the pace of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
As a result, the organizations will have to develop solutions for these major problems.
Challenges in Implementing 4IR, Especially for Developing Countries
Developing countries and third world Countries will not implement these new technologies without a challenge. This fact is especially true for both sides. The following challenges will impact the adoption of 4IR in developing countries.

Lack of Skilled Workers
The new industries created by the Fourth Industrial Revolution consisted of advanced fields. Consequently, workers need significant education and training to be competent in these fields.
Unfortunately, there isn’t an education pathway for developing nations in these fields. So, they will face a brain drain, with workers leaving.
So, what can we do about the lack of skilled workers or opportunities to get educated in these new fields? The answer is simple but not easy to put in place.
First, universities need to introduce AI, IoT, and Robotics subjects. Furthermore, students will not join these courses if they are unsure of getting hired.
As a result, this leads to the next challenge of the 4th Industrial Revolution: Developing the Infrastructure.
Digital Infrastructure Development
Digital infrastructure is the physical foundation of these new technologies. Infrastructure gives access to the Internet, Data Centers, the Cloud, and storage.
Access to powerful computers may not be available for individuals or small businesses. However, these individuals can access cloud computing to meet their requirements.
Cloud computing can provide services such as Machine Learning and Analytics. So, developing countries need to build server farms to provide cloud computing with better Internet speeds to access such features.
Improving the infrastructure will also contribute to new jobs. The reason is that workers will be needed to maintain the new facilities.
Opportunities of Fourth Industrial Revolution / 4IR / Industry 4.0
Despite the major challenges discussed above, there is much room to grow. Therefore, countries embracing the Fourth Industrial Revolution can enjoy the opportunities by adopting Fourth Industrial Revolution.

These opportunities are available to different sectors, including Manufacturing, Agriculture, and many more.
Opportunities of 4th Industrial Revolution for Manufacturing
The “smart factory” is one of the important innovations in Industry 4.0. Smart Factories will operate the production facilities and logistics systems without human intervention. And by utilizing the Internet of Things (IoT), smart factories will provide more production in less time.
IoT allows factory devices such as tools and robots to communicate. Therefore, the exchange of data between devices is important. As a result, the supply chain is better organized within the smart factory.
Modularity is a key aspect of the smart factory. The modular smart factory uses the IoT to control the physical process of the factory floor. So, it can virtually simulate the physical world for better production.
Furthermore, IoT has smart sensors attached to devices in the manufacturing process. Therefore, it can diagnose physical problems before they occur by using Artificial Intelligence.
Opportunities of 4th Industrial Revolution in Agriculture
According to research, the demand for food is increasing. As a result, the production capacity needs to grow by 70 percent in the next 30 years. Therefore, the agricultural industry must adopt the Fourth Industrial Revolution to maximize crop production. Reference: Global agriculture towards 2050
Robotics can play a major role in agriculture. For example, robots can be used in the process of pruning, weeding, and monitoring crops. The efficacy of these processes will thus increase. Using IoT in agriculture will also increase efficiency.
Economic Opportunities of the 4th Industrial Revolution
Embracing the Fourth Industrial Revolution can further boost the economy. According to a survey, IoT will improve the economy by 2030. Reference: The Internet of Things and connected devices
The US is estimated to grow by $ 7.1 billion in new technologies. Next is China with $ 1.8 trillion, Germany with $ 700 billion, and the UK with $ 531 billion.
These are huge gains for the developed nations that can capitalize on 4IR. Also, the survey shows the value added to the GDP by manufacturing.
For example, Germany had production contribute 22% of their GDP. Meanwhile, the US had 12% added from manufacturing production.
Thus, the 4th Industrial Revolution presents huge economic opportunities for countries.
Business Opportunities of the 4th Industrial Revolution
Businesses can find many opportunities in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. These opportunities are common for a variety of industries, such as:
- Efficiency: by saving raw materials and energy
- Productivity: using intelligent technology such as AI and IoT is more productive
- Flexibility: using cyber-physical systems provides better flexibility
- Individualization on demand: customer demand is found by technology
- Decentralization: quicker and data-driven decision-making
Businesses, as a result, will benefit from implementing the technologies of the 4th Industrial Revolution.
Opportunities of 4IR for Developing Nations
Developing nations have some unique opportunities to grow. So what are the opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution for developing nations?

Generating Economic Growth
The introduction of emerging technologies is sure to come to developing countries soon. As a result, this will give rise to new fields and job opportunities for the population.
To capitalize on this opportunity, governments need to encourage investment. These new technologies have much economic potential.
Economic development will be rapid if local and foreign investment increases. Thus, millions of lives could improve in the 4th Industrial Revolution.
Modernizing Healthcare
As technology advances at an ever-faster pace, Healthcare is being transformed. Digitizing healthcare records will make diagnosing and treating people an easier task.
Furthermore, Autonomous vehicles such as drones may transport medicines to the desired destination. Using AI, vaccines, and medicines will speed up the time to develop medication.
Healthcare, as a result, has the potential to save more lives than ever before. This point is also true for developing countries where child mortality will reduce.
Overcoming Poverty, Inequality, and Unemployment
New jobs from the Fourth Industrial Revolution will reduce poverty, inequality and unemployment.
Furthermore, food stocks may increase due to using AI and IoT in the Agri sector. The increasing availability of food stocks will help fight inequality in resources.
With the growth of the Internet, access to information is becoming easier. As a result, ignorance will reduce among the poor populations of third-world countries.
Impact of the Fourth Industrial Revolution on Least Developed Countries (LDCs)
The Least Developed Countries (LDC) are considered the lowest developed countries. These countries have a basic command of technology.

LDCs are still using incomplete 3IR technologies. So, these countries will find it difficult to embrace the new technologies of the 4IR.
The adoption of new technologies is not even across industries. For example, computers, machinery, and transportation have high adoption rates.
Industries that are not currently using technologies will fall behind. They must accept digitization to expand their businesses.
These countries should focus on gradually integrating new technologies.
Potential Risks from the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Risks from the Fourth Industrial Revolution are like the challenges discussed earlier. These include rising unemployment, inequality, income stagnation, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities.

Rising Unemployment, Inequality and Income Stagnation
For all the benefits that the Fourth Industrial Revolution can bring, its drawbacks are:
- Having technology replace the regular workers will make those workers redundant. The result would be mass unemployment for millions of people.
- Inequality is the gap in living standards between the wealthy and the poor. Thus, the working class will face an uncertain future.
- Income stagnation will happen if technology takes over. Since technology can work, humans will earn less, even in developed countries.
Cybersecurity Vulnerability
In today’s connected world, the risk of data breaching and hacking is more likely. People with malicious intentions can do more damage.
So, the increased adoption of data analytics and machine learning risks privacy more. In that sense, AI and advanced algorithms can breach data.
People are further concerned about increased surveillance by governments. They track the population via their connected devices. Thus, this leads to security issues, making people concerned about breaches.
Cyber security vulnerabilities need to be addressed for the 4th Industrial Revolution to succeed.
Ecological Risks
New technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution used large amounts of power. And they will need more raw materials to build the infrastructure.
Power generation using fossil fuels is harmful to the environment. So, by adopting 4IR, releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere will contribute to global warming.
Rapid Industrialization and the development of technology are happening already, leading to urbanization and excessive deforestation.
Solutions to Overcome the Risks of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
We need to find solutions to reduce these risks from becoming a reality. First, governments should invest in education and training for people of all ages. This will better prepare them for new technologies and digitization.

Besides, practical training of the current workforce through reskilling programs needs doing. This way, workers are better adapted to be competitive in the new market.
The education system needs to incorporate practical training for young people, including children. Thus, they will have the required knowledge to join the workforce in Industry 4.0.
As a result, STEM fields need to focus on the education sector.
There needs to be transparency in the case of cybersecurity. For example, Facebook owns large amounts of personal data. They provide no-cost services.
In this situation, the customers are the product. Customer data is given over to advertisers. Thus, authorities need to create strict laws to prevent malicious groups’ data violations.
How Can Businesses Cope to Make the Most of 4IR?
Businesses are a core part of the free-market economy. Thus, they must cope with the changes of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. A business creates value through work by the employees, utilizing tools to aid them.

With the introduction of Industry 4.0, this value creation method is changing. Advanced technologies push new opportunities, connecting data, people, and objects.
It’s changing the way manufacturers work and how customers use products. Thus, businesses need to introduce new business models to adapt to the changes.
Changing Mindset from Product to Service
Manufacturers that want to cope with Industry 4.0 must redefine themselves. For example, they can add services to their products.
Companies will evolve as product-specific companies. As a result, they can reduce time and cost by changing from exclusive manufacturers.
Due to this, there is an acceleration in adopting the product-service system (PSS). PSS packages together products and services for customers. A current example of PSS is Tesla Cars.
The car gets added functionalities through software updates every day.
Implementing PSS has increased interactions between a company and the customer. Thus, this can open up new revenue streams.
Enhance Customer Experience
Customers have always been the most important component of a business. Developers can further enhance customer experience by leveraging these emerging technologies.
These technologies include Big Data, Augmented Reality (AR), and Virtual Reality (VR). As a result, businesses can find new ways to engage the customer and improve the user experience.
Companies can better understand what customers need and want by using the data.
As a result, companies will respond immediately to the customers’ needs and wants. An example is using social media polls to make them the more popular decision.
Develop Smarter Products
With the rapid increase of new technologies, products need to provide better experiences. So, the Fourth Industrial Revolution will enable smarter products.
Smart products are hybrid products. The physical product has added electrical components for connecting to the digital world. As a result, motor vehicles, medical devices, and smart packaging are made smarter.
The benefits of using smart products are better suited for the purpose. They make the customer’s life easier and improved.
Also, the product can get more support. In addition, data collected on products can provide intelligence. Using the information can help prevent failures and downtime.
A smart, product-centric ecosystem in 4IR presents opportunities to create new business models. Also, it can develop better products that align with customers’ needs.
Business Models Changes for the 4th Industrial Revolution
Businesses have to adapt and offer a variety of business models. To capture the most market share, they will need to cater to customers. Some of these business models in the Fourth Industrial Revolution include:
Freemium Model
In this model, the product is free to use. However, they must pay a “premium” to use advanced features.
An example of this is Zoom. Zoom can be used for free by its users. However, users need to pay for unlimited meeting times.
Subscription Model
In the subscription model, the business charges a flat fee. In return, the customer gets unlimited access for the time. An example of this is Netflix. Users can pay monthly for unlimited use.
Free Offerings
This business model offers its services for free to the customers. However, they make money in other ways by offering ads.
A good example is Facebook, which is free to use. However, they sell users’ data for marketing purposes to make money.
Marketplace Model
This business model connects buyers and sellers on a common platform. An example of this is eCommerce platforms such as Amazon. As a result, the platform can be the middleman between buyers and sellers.
User Experience Premium Model
The User Experience is the primary focus of this model. Companies such as Tesla offer a unique user experience, which helps them stand out.
They provide an easier buying experience. Furthermore, Tesla provides software updates to improve the functionality of the car.
As a result, businesses can adopt a variety of business models. But, first, they need to select the appropriate models to ensure that they don’t fall behind. Business Success in the Fourth Industrial Revolution depends on adopting these business models.
Which Country is the Current Leader in the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Countries have been adopting the Fourth Industrial Revolution at their convenience.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) has created a new benchmarking framework for diagnostic tools and data sets. The framework determines the current level of readiness for adopting Industry 4.0.

They have published all this in a report titled “Readiness for the Future of Production.”
Germany
Germany has the 4th largest manufacturing sector in the world. Besides, they launched Industry 4.0 in 2011. Thus, Germany has been a leader in adopting the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The Germans have a strong focus on Technology and Innovation. They have strong educational and technical training programs too. As a result, Germany has a capable current workforce.
Japan
According to the report, Japan is the leading nation in being “ready” for future work. This is due to Japan currently having the 3rd largest manufacturing sector globally.
Also, the Government has launched Society 5.0 to improve Japan by using technology to transform production and society.
The Japanese Government and their industries have also worked together. It is called Connected Industries. Their goal is to connect different sectors of the economy.
China
The Chinese have the largest manufacturing sector in the world. China has gradually evolved its capabilities over the last two decades.
As a result, China has moved from making low-cost goods to more advanced products.
The Chinese Government launched “Made in China 2025” in 2015. The goal of this movement is to upgrade China’s manufacturing sector.
China is expected to be the leader in manufacturing innovation. So, they took the lead in the 4th Industrial Revolution early.
The Future of Work – Are We Prepared?
Over the last twenty years, new technology has caused some jobs to become obsolete. However, it has also created new, previously unheard-of job titles.

For example, online flight comparison sites have made physical travel agents unnecessary. So, new technologies in 4IR have led to new jobs not existing before.
The new jobs include app developers, social media marketers, and data scientists. So, will these changes improve or hinder the future of work?
As discussed in this article, Automation will take over millions of human jobs. The approximation is that by 2030, robots will replace 800 million human jobs.
Those working in Automation need to be ready to lose their main job. But, in addition, workers need to prepare to learn new skills fitting the new upcoming reality.
However, with the disappearance of old jobs comes new roles. These new roles are a direct result of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Fields such as AI, ML, Data Science, and Robotics need fresh people willing to take them further.
These fields are getting massive investments from governments and the private sector. As a result, these fields will see unfiltered growth. But on the other hand, Savvy individuals need to be ready to capitalize on these emerging fields.
So, Are We Ready for the 4th Industrial Revolution?
The World Economic Forum conducted a study titled “Future of Jobs Survey 2018”. This study analyzes the future of the workplace due to the adoption of 4IR. The report highlighted some roles which are likely to become redundant.
The redundant roles include:
- Data Entry Clerks
- Accounting Clerks
- Administrative Secretaries
- Assembly and Factory Workers
- Cashiers and Ticket Clerks
- Bank Tellers
- Car, Van, and Motorcycle Drivers
- Telemarketers and more.
These roles, and a few more, are at risk in the future. Therefore, the workers of these jobs need to find a way to pivot to the new and upcoming job roles.
However, it isn’t all easy. Education and training need to be at the forefront to adapt to the new fields. These fields include Data Analysts, AL and ML Specialists, and Robotics Engineers.
What is the Next Industrial Revolution?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is currently ongoing. 4IR is mechanizing everything and making products and factories “smart.” However, the next Industrial Revolution is right around the corner.
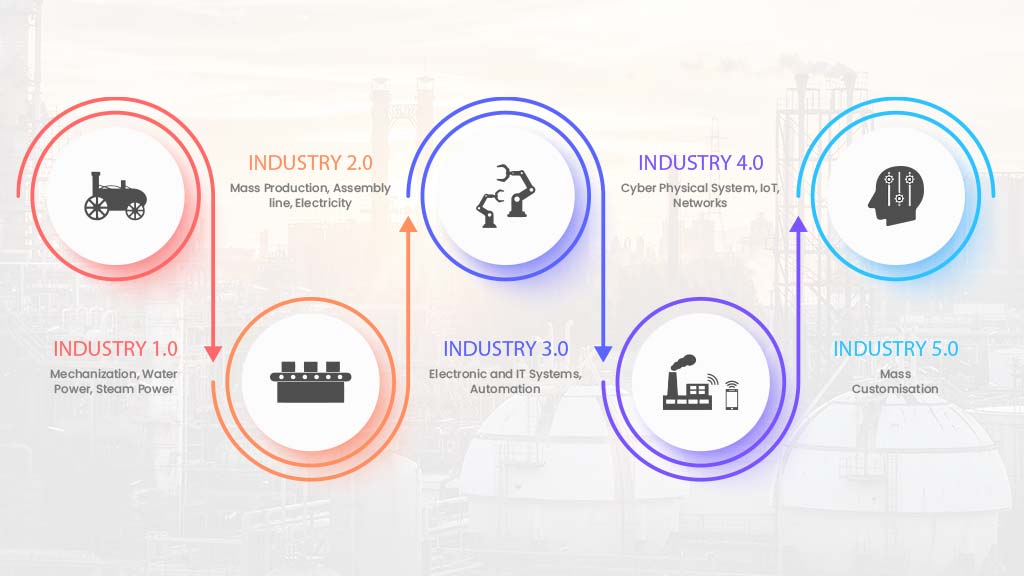
The next revolution will continue keeping technology as a catalyst and a driver. But the aim is to keep the general welfare of the members of the society at the forefront.
As a result, it creates a blend of a super-intelligent society-technology ecosystem. Industry 5.0 will take Industry 4.0 and place the human being at its center.
Making innovation and purpose a priority will allow humans to work alongside technology. Thus, this will lead to an era of making technologies such as robots to take care of repetitive tasks.
Humans will work on more creative and complex tasks. So, the people will work remotely more. Technology will enable them to complete their work from the comfort of their homes. An example of this can be the recent announcement of Facebook’s Metaverse.
Thus, the Fifth Industrial Revolution will result in more advanced collaborations. Humans, machines, processes, and systems will work together for optimal performance.
Conclusion
The Fourth Industrial Revolution brings forward new opportunities for the future. It can lead to prosperity in many fields, including Healthcare, transportation, and homes.
However, the potential pitfalls cannot be ignored by leaders. It is up to world leaders and governments to enact policies to make the best of this brave new world.
You might now be thinking, what can I do to help?
Well, the key is people. We, as individuals, each have the responsibility to think about our future. Our goal should be to shape it to benefit the next generation. 4IR is relevant to our lives even today, and we must not waste any time trying to implement changes.
Fourth Industrial Revolution FAQs
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is a new term for many people. As a result, you may have some questions about this emerging field. Thus, I have compiled a shortlist of FAQs to answer your queries.
In his article for Foreign Affairs, the term Fourth Industrial Revolution was officially used in 2015 by Klaus Schwab, executive chairman of the WEF – World Economic Forum.
The four Industrial Revolutions are:
First Industrial Revolution: coal and steam
Second Industrial Revolution: gas and electronics
Third Industrial Revolution: digital Computing and the Internet
Fourth Industrial Revolution: IoT, Automation, and AI
The Fourth Industrial Revolution includes many emerging technologies, including:
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Internet of Things (IoT)
3D Printing
Robotics
Quantum computing
And many more
Productivity of the workforce will increase. Using technology, more people will benefit from smarter products and services. People will need to prepare to grab these new opportunities in 4IR.
The important thing to do is to gain knowledge about these new advancements. We should engage in productive conversations with our friends and family. Thus, this will raise awareness of the capabilities available in 4IR to us today.
The next industrial revolution, Industry 5.0, will build upon the Fourth Industrial Revolution. So, 5IR will include smart technologies like AI, IoT, Robotics, and Automation to incorporate greater human intelligence.
The main difference between the Fourth and Fifth industrial revolutions is that Industry 5.0 aims for better working relationships between smart technologies and humans. Thus, instead of humans competing with technologies for jobs, they will work harmoniously.
4IR technologies have a place in the education section. For example, students can learn and research in massive open online courses (MOOCs) with virtual Classrooms, Laboratories, Libraries, Teachers and more
Education providers like schools, colleges, and universities can implement the following changes:
Improve STEM education, Promote school makerspaces, Redefine the purpose of education, Alter educator training, Develop human potential.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution will change society forever. However, we need to look out for some drawbacks to make adjustments.
Cybersecurity Risk
Ethical Issues with AI, Gene Editing
Rising Inequalities
Core Industry Disruptions
4IR presents individuals, businesses, and governments with many opportunities for a better future. They include:
Lower barriers between inventors and the market
Increased use of AI for smart solutions
Integration of different domains for fusion
Improved quality of life with advanced robotics
More connection between people due to the Internet
Four major technological developments drive the 4IR:
High-speed mobile Internet (5G)
AI, Automation, and Robotics
Big data analytics
Cloud technology
One of the main outcomes of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is improved human productivity. With technologies like AI and Automation helping our daily lives, people make smart choices faster than ever before.
Robots will take over many manual and repetitive jobs. As a result, workers in those jobs will be most at risk.
However, other workers will benefit from robots freeing up menial jobs. They will be able to focus on smarter solutions.
The economy will benefit from the creation of new jobs due to 4IR, which will lead to economic growth in technological sectors. As a result, the whole economy will grow.
The 4th Industrial Revolution can potentially reduce air pollution and decarbonize the economy. It can be done by:
Smarter Air Monitoring Systems
Using Robots and Drones to Clean up the Environment
Automated transportation reduces the need for personal vehicles
Using Big Data and Blockchain to make smarter decisions
With smarter technologies and remote work, companies can work with each other easier than ever before. Thus, the 4th Industrial Revolution enables businesses to collaborate more effectively – increasing globalization.
